
These techniques are not complicated, but they can still confuse beginner malware analysts and reverse engineers. One common method to alter the code execution path is through SEH (Structured Exception Handling). A simple example is shown below:
If an analyst single-steps through the code, they will lose control.
However, there are other ways to achieve similar results using Windows API functions with callbacks. These callbacks can be utilized to hinder an analyst’s progress.
ReadFileEx and WriteFileEx are asynchronous counterparts to ReadFile and WriteFile. The interesting aspect is that they call the lpCompletionRoutine completion routine when the writing or reading is completed or canceled:

VOID CALLBACK FileIOCompletionRoutine( _In_ DWORD dwErrorCode, _In_ DWORD dwNumberOfBytesTransfered, _Inout_ LPOVERLAPPED lpOverlapped){ MessageBox(0, L"File I/O operation completed.", L"Notification", 0);}
int main(){ const auto hFile = CreateFile(L"test_test", GENERIC_ALL, 0, nullptr, CREATE_ALWAYS, FILE_FLAG_DELETE_ON_CLOSE | FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED, nullptr);
OVERLAPPED ov{ 0 }; WriteFileEx(hFile, "test", strlen("test"), &ov, FileIOCompletionRoutine);
SleepEx(0, TRUE);
return 0;}In this case, the analyst also loses control.
What about EnumDisplayMonitors?

Note: We can stop the enumeration by returning FALSE.
There are many other functions that can be used similarly, such as EnumWindowStations, EnumDesktops, EnumDesktopWindows, EnumThreadWindows, EnumWindows, EnumChildWindows, EnumResourceTypes/Ex, EnumResourceNames/Ex, EnumResourceLanguages/Ex, EnumDirTree, AddSecureMemoryCacheCallback, SetThreadpoolTimer/Ex, SetThreadpoolThreadMinimum, SetThreadpool, StackWalk64/Ex, EnumerateLoadedModulesEx, and EnumerateLoadedModules64. Just explore a bit with MSDN.
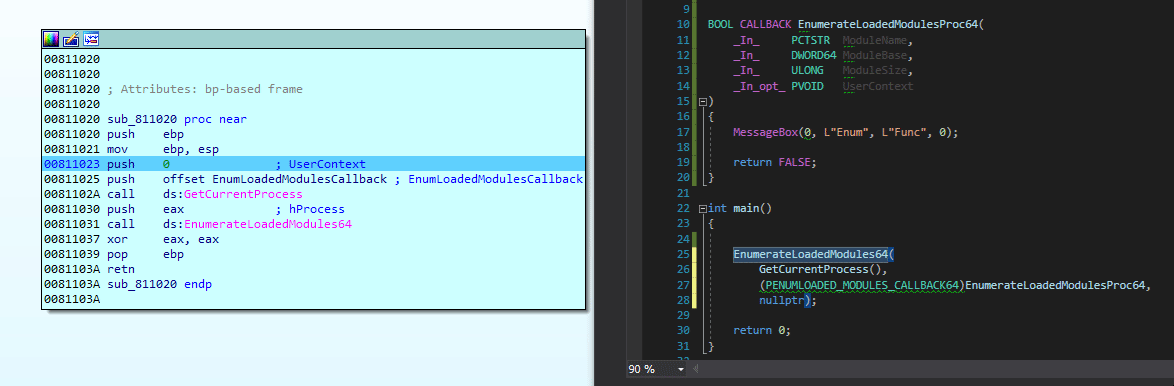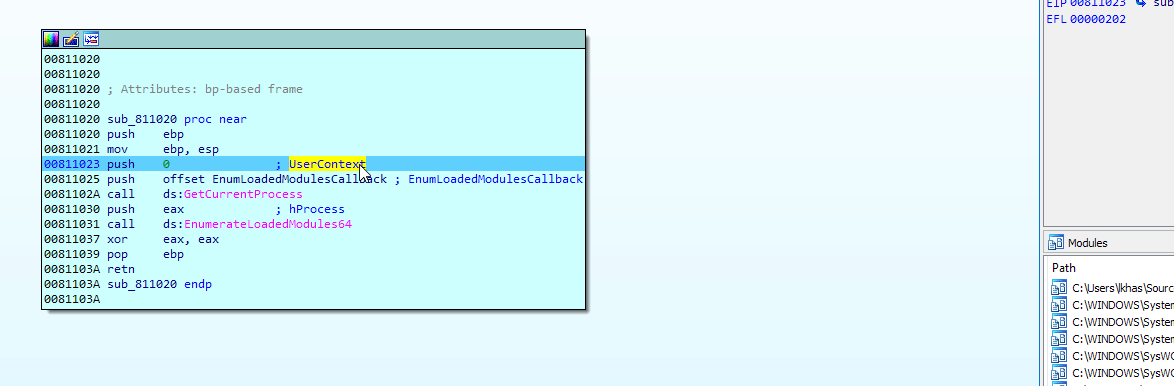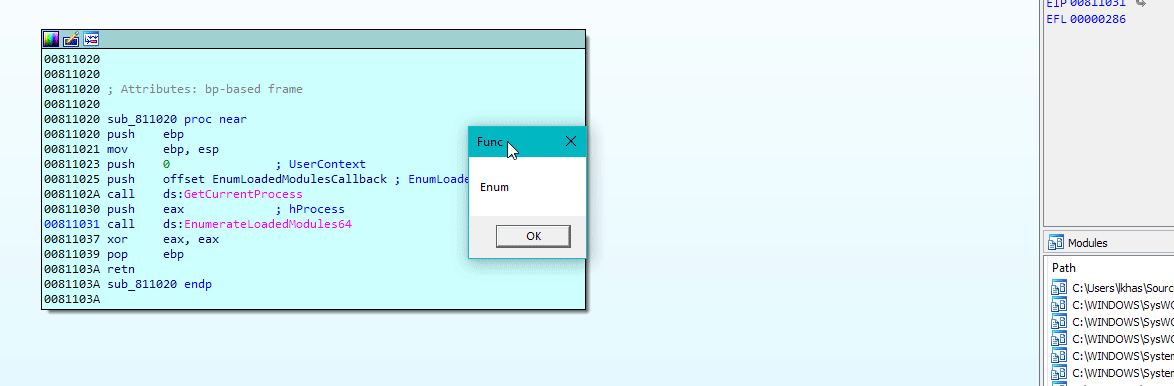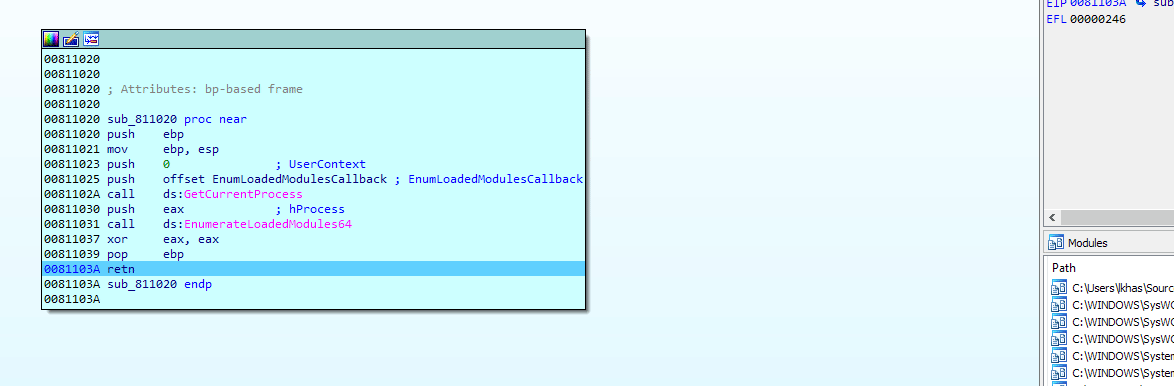
BOOL CALLBACK EnumerateLoadedModulesProc64( _In_ PCTSTR ModuleName, _In_ DWORD64 ModuleBase, _In_ ULONG ModuleSize, _In_opt_ PVOID UserContext){ MessageBox(0, L"Enumerating Loaded Module", L"Notification", 0); return FALSE; // Stop enumeration}
int main(){ EnumerateLoadedModules64( GetCurrentProcess(), PENUMLOADED_MODULES_CALLBACK64(EnumerateLoadedModulesProc64), nullptr);
return 0;}